Product Description
Product Description
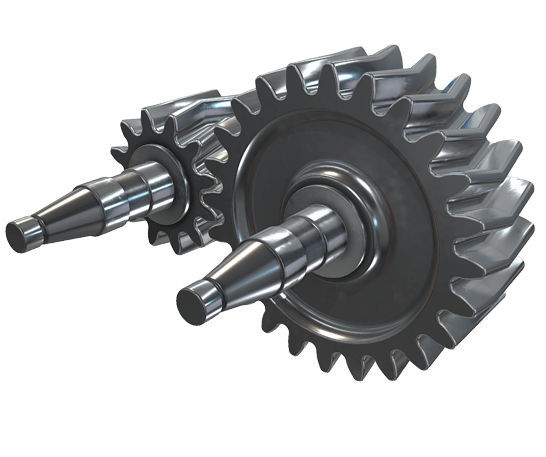
Herringbone gears are a specific type of gear that feature a unique double helix shape resembling the bones of a fish, hence the name “herringbone.” They are characterized by their distinctive V-shaped teeth that are arranged in a herringbone pattern.
Features
Double Helix Shape: The most distinctive characteristic of herringbone gears is their double helix shape, which allows for smoother and more efficient operation compared to traditional spur gears.
Self-Aligning: Due to the opposing helix angles on either side of the gear, herringbone gears are self-aligning. This helps to reduce axial thrust and prevents gear misalignment.
High Load Capacity: Herringbone gears are capable of handling high loads and transmitting significant amounts of power due to their robust design.
Reduced Vibration and Noise: The double helix design helps to cancel out axial forces and minimize vibration and noise during operation, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction is important.
Functions
Power Transmission: Like other types of gears, herringbone gears are primarily used to transmit power between parallel shafts while maintaining a constant speed ratio.
Direction Change: Herringbone gears can change the direction of rotation between 2 shafts while transmitting power efficiently.
Speed Reduction or Increase: By using herringbone gears with different numbers of teeth on the mating gears, speed reduction or increase can be achieved.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machinery |
|---|---|
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cast Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Double Helical Gear |
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
| Transport Package: | Wooden Case |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How do you choose the right size herringbone gear for your application?
Choosing the right size herringbone gear for your application involves considering several factors and performing engineering calculations. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in selecting the appropriate size herringbone gear:
- Determine the Application Requirements: Start by understanding the specific requirements of your application. Consider factors such as the input and output speeds, torque loads, power requirements, duty cycle, and operating conditions. Determine the desired service life, efficiency, and reliability expectations for the gear system.
- Calculate the Gear Ratios: Determine the required gear ratios based on the speed and torque requirements of your application. Gear ratios define the relationship between the rotational speeds and torques of the input and output shafts. Select appropriate gear ratios that fulfill the desired performance objectives.
- Calculate the Load and Torque: Estimate the maximum load and torque that the herringbone gear will experience during operation. Consider both static and dynamic loads, shock loads, and any potential overload conditions. Calculate the required torque capacity of the gear system based on these load considerations.
- Consider the Size and Space Constraints: Evaluate the available space and size constraints in your application. Measure the available distance for gear installation, including the gear’s diameter, width, and axial length. Consider any restrictions on the gear’s physical dimensions and ensure that the selected gear size fits within the available space.
- Determine the Gear Module: The gear module is a parameter that defines the size and number of gear teeth. Calculate the gear module based on the desired gear ratios, torque capacity, and available space. The gear module is typically determined by considering a balance between gear tooth strength, contact ratio, and manufacturing feasibility.
- Perform Gear Design Calculations: Utilize standard gear design formulas and calculations to determine the required number of gear teeth, pitch diameter, helix angles, and other gear dimensions. Consider factors such as gear tooth strength, contact ratio, tooth profile optimization, and gear manufacturing standards. These calculations ensure that the selected gear size can handle the anticipated loads and provide reliable performance.
- Consult Manufacturers and Standards: Consult gear manufacturers, industry standards, and guidelines to ensure compliance with best practices and safety requirements. Manufacturers can provide technical expertise, recommend suitable gear sizes, and offer guidance on material selection, heat treatment processes, and gear quality standards.
- Consider Cost and Availability: Evaluate the cost implications and availability of the selected gear size. Consider factors such as material costs, manufacturing complexity, lead times, and the overall economic feasibility of the gear system. Balance the desired performance with cost considerations to arrive at an optimal gear size.
It’s important to note that selecting the right size herringbone gear requires expertise in gear design and engineering. If you lack the necessary knowledge, it is advisable to consult with experienced gear engineers or manufacturers who can assist in the selection process.
In summary, choosing the right size herringbone gear involves determining the application requirements, calculating gear ratios and torque loads, considering size constraints, determining the gear module, performing gear design calculations, consulting manufacturers and standards, and considering cost and availability. Following these steps ensures that the selected herringbone gear size meets the specific needs of your application and provides reliable and efficient operation.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of using herringbone gears?
Herringbone gears offer several advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when evaluating their suitability for a specific application. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of using herringbone gears:
Advantages of Herringbone Gears:
- Reduced Friction: The double helical arrangement of the teeth in herringbone gears helps cancel out axial thrust and minimize sliding friction during gear meshing. This results in reduced frictional losses, improving overall efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
- Smooth Operation: Herringbone gears provide smooth and quiet operation due to their gradual meshing and unmeshing characteristics. The opposing helix angles of the teeth enable smooth tooth engagement, reducing impact and vibrations, and enhancing overall system performance.
- High Torque Capacity: Herringbone gears have a larger surface area of contact compared to spur gears, allowing them to transmit higher torque loads. This higher torque capacity enables the use of more compact gear designs and reduces the need for additional gear stages, resulting in space and weight savings.
- Better Load Distribution: The double helical tooth arrangement in herringbone gears distributes the load more evenly across the gear face. This improves load-bearing capabilities, reduces stress concentrations, and enhances gear life and durability.
- Improved Alignment: Herringbone gears are self-aligning to a certain extent due to their double helical structure. This makes them more forgiving of minor misalignments, simplifying the alignment process during installation and reducing the risk of gear tooth damage.
- No Axial Thrust: The opposing helix angles of the teeth in herringbone gears cancel out the axial thrust. This eliminates the need for additional thrust bearings or complicated thrust balancing mechanisms, simplifying the overall gear system design.
Disadvantages of Herringbone Gears:
- Complex Manufacturing: Herringbone gears are more complex to manufacture compared to spur gears. The double helical tooth profile requires precise machining and specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase production costs.
- Tighter Tolerance Requirements: The double helical tooth profile of herringbone gears requires tight manufacturing tolerances to ensure proper gear meshing and alignment. This may require more stringent quality control measures during production and assembly.
- Increased Axial Space: Herringbone gears require additional axial space compared to spur gears due to their double helical structure. This can be a constraint in applications with limited axial space availability, requiring careful consideration during system design.
- Higher Complexity in Gearbox Design: Incorporating herringbone gears into a gearbox design can add complexity to the overall system. The need for proper gear alignment, balancing, and lubrication may require more sophisticated gearbox configurations and maintenance procedures.
- Specialized Maintenance: Herringbone gears may require specialized maintenance procedures, such as gear tooth inspection, alignment checks, and lubrication. This can involve additional time and effort compared to simpler gear systems.
When considering the use of herringbone gears, it is essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application, including load capacity, operating conditions, space constraints, and cost considerations. Proper design, manufacturing, and maintenance practices can help leverage the advantages of herringbone gears while mitigating their disadvantages.

Can you explain the unique shape of herringbone gear teeth?
The unique shape of herringbone gear teeth is a defining characteristic of herringbone gears, also known as double helical gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of the unique shape of herringbone gear teeth:
Herringbone gears have a V-shaped or herringbone-shaped tooth profile, which is formed by two helical gear sections that are mirror images of each other. This tooth profile is distinct from the straight or helical tooth profiles found in other types of gears such as spur gears or helical gears.
When viewed from the end, the teeth of a herringbone gear resemble the letter “V”. This shape is created by the combination of two opposing helix angles, one on each side of the gear. The helix angle refers to the angle at which the teeth are inclined relative to the gear’s axis.
In a herringbone gear, the helix angle of one helical section is opposite in direction to the helix angle of the other helical section. This means that as the gear rotates, the teeth on one side lean in one direction, while the teeth on the other side lean in the opposite direction.
The opposing helix angles of the two gear sections in herringbone gears serve several important purposes:
- Axial Thrust Elimination: One of the main advantages of the herringbone gear design is the elimination of axial thrust or end thrust forces. In helical gears, the helix angle of the teeth generates an axial force along the gear’s axis during rotation. However, in herringbone gears, the opposing helix angles cancel out these axial forces, resulting in a balanced gear that does not experience significant axial movement or require thrust bearings.
- Smooth Engagement: The opposing helix angles of herringbone gears facilitate smooth and gradual tooth engagement. As the gear rotates, the teeth on one side gradually come into contact with the teeth on the other side. This gradual meshing reduces sliding friction, minimizes backlash, and ensures a continuous and smooth transfer of power between the gear sections.
- Increased Load Capacity: The V-shaped tooth profile of herringbone gears provides increased tooth contact area compared to gears with straight or helical teeth. This increased contact area improves load distribution and allows herringbone gears to handle higher torque loads, resulting in an increased load-carrying capacity.
The unique shape of herringbone gear teeth requires precise manufacturing techniques to ensure proper meshing and alignment of the gear sections. The teeth must be accurately machined to achieve the correct helix angles and tooth profiles, ensuring smooth operation and efficient power transmission.
In summary, the unique shape of herringbone gear teeth, with their V-shaped or herringbone-shaped profile formed by opposing helix angles, enables axial thrust elimination, smooth engagement, and increased load capacity. These characteristics make herringbone gears well-suited for applications where efficient torque transmission, balanced operation, and high load-carrying capacity are essential.


editor by CX 2024-04-17