Product Description
Metric Hobbing Carbon Alloy Steel Precision Gearbox Reducer Herringbone CNC Machining Auto Spare Parts Metal Transmission Drive OEM Grinded Miter Helical Gear
Features
1. High precision gear for smooth, quiet operation.
2. Flexible for custom-made requests.
3. Stable transmission, low impact, vibration and noise.
4. Heavy Load capability, more compact, but less complex.
Product Description
| Products | Spur Gear, Helical Gear, Herringbone Gear, Spiral Bevel Gear, Straight Bevel Gear, Worm Gear, Shaft, Pinion |
| Module | M0.3-M10 |
| Precision grade | DIN6, DIN7, DIN8, DIN10 |
| Pressure angle | 14.5 degree, 15 degree, 20 degree |
| Material | Medium Carbon Steel: 35#, 45# Carburizing Steel: 20CrMnTi, 20CrMnMo, 20CrMo Alloy Steel: 40Cr, 35CrMo, 42CrMo, 40CrNiMo Cast Iron: HT250, QT400 Copper, Stainless Steel, Brass, Nylon, POM, and so on |
| Heat treatment | Hardening & Tempering, Surface Quenching, Integral Quenching, Carburizing Quenching, Tempering, Normalizing, Nitriding |
| Surface treatment | Blacking, Polishing, Anodization, Chrome Plating, Zinc Plating, Nickel Plating |
| Application | Gearbox and reducer; Precision cutting machines, Lathes machines; Milling machines; Grinder machine; Automated mechanical systems; Automated warehousing systems. Gear hobbing machines, gear shapers, gear shaving machines, gear milling, gear grinding machines and many kinds of gear-related machines. |
| Machining process | Forging, Machining, Hobbing, Milling, Shaving, Grinding, Heat treatment… |
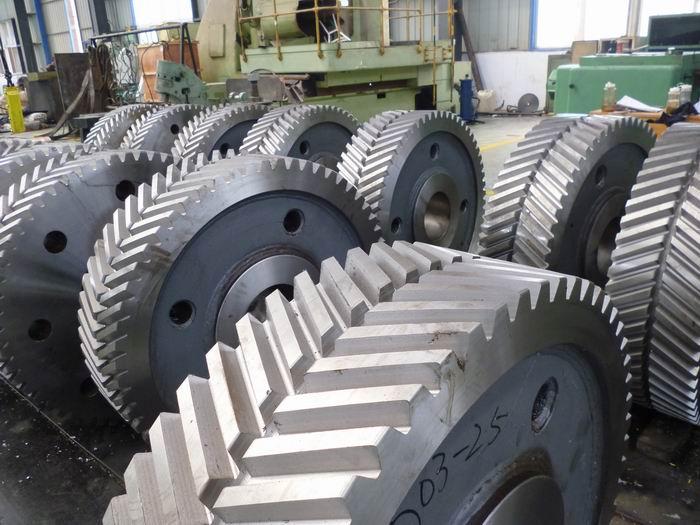
Detailed Photos
Our Advantages
Related Product
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: How to ship the planetary gear to us?
A: It is available by air, sea, or train.
Q: How to pay the money?
A: T/T and L/C are preferred, with different currencies, including USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know if the product is suitable for me?
A: >1ST confirm drawing and specification >2nd test sample >3rd start mass production.
Q: Can I come to your company to visit?
A: Yes, you are welcome to visit us at any time.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machinery, Helical Gearbox |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample helical gear
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you install a herringbone gear system?
Installing a herringbone gear system requires careful attention to ensure proper alignment, engagement, and functionality. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in installing a herringbone gear system:
- Preparation: Before installation, gather all the necessary components, including the herringbone gears, shafts, bearings, and any associated hardware. Ensure that the gears and shafts are clean and free from any debris or contaminants that could affect their performance. Review the gear system’s specifications, including the gear ratios, torque requirements, and any specific installation guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
- Shaft Alignment: Proper shaft alignment is crucial for the smooth operation of a herringbone gear system. Align the shafts accurately to ensure that they are parallel and concentric with each other. This can be achieved using alignment tools such as dial indicators and laser alignment systems. Proper shaft alignment helps to minimize misalignment-related issues such as gear tooth wear, noise, and premature failure.
- Gear Engagement: Position the herringbone gears on their respective shafts, ensuring that they are correctly oriented and meshing properly. The double helical tooth profile of the herringbone gears requires careful engagement to prevent interference and ensure smooth operation. Pay attention to the gear backlash, which is the slight clearance between the gear teeth when they are not under load. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate gear backlash and adjust as necessary.
- Bearing Installation: Install the appropriate bearings to support the gear shafts. Ensure that the bearings are aligned and properly seated in their housings. Use the specified lubrication method and apply the appropriate lubricant to the bearings to minimize friction and wear. Adequate lubrication is essential for the smooth operation and longevity of the gear system.
- Check Clearances: Once the gears, shafts, and bearings are installed, check for any interferences or clearances issues. Verify that there is sufficient clearance between the gear teeth, as well as between the gears and any adjacent components or structures. Ensure that there are no obstructions that could impede the rotational movement of the gears or cause damage during operation.
- Tightening and Fastening: Securely tighten all fasteners, such as bolts or set screws, to hold the gears, shafts, and bearings in place. Follow the recommended torque specifications provided by the manufacturer to ensure proper fastening without over-tightening, which could lead to excessive stress or deformation of the components.
- Testing and Adjustment: After installation, perform a thorough inspection and functional testing of the herringbone gear system. Rotate the shafts manually or using a suitable drive mechanism to check for smooth and proper gear engagement. Listen for any unusual noises, vibrations, or irregularities that could indicate misalignment or other issues. If necessary, make fine adjustments to the gear engagement, backlash, or shaft alignment to optimize the performance of the gear system.
It is important to note that the installation process may vary depending on the specific gear system design, size, and application requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines, technical documentation, and any applicable industry standards when installing a herringbone gear system to ensure proper installation and optimal performance.
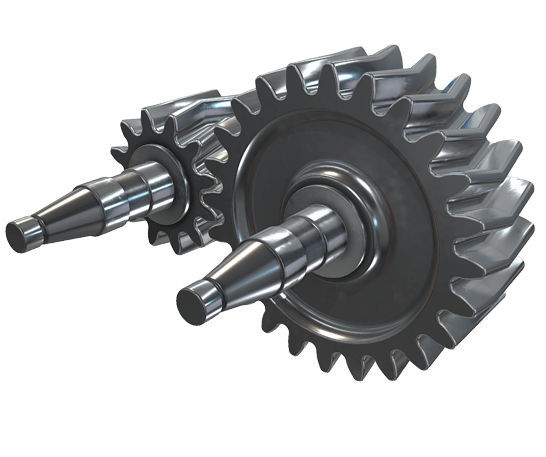
Are herringbone gears suitable for high-torque applications?
Herringbone gears are well-suited for high-torque applications due to their design characteristics and advantages. Here’s a detailed explanation of why herringbone gears are suitable for high-torque applications:
- Large Surface Area of Contact: Herringbone gears have a larger surface area of contact between the gear teeth compared to conventional spur gears. This increased contact area allows herringbone gears to distribute the torque load more effectively. The larger contact area helps prevent tooth deflection and distributes the load across a greater number of teeth, resulting in improved torque transmission capabilities.
- Higher Torque Capacity: The design of herringbone gears enables them to handle higher torque loads. The opposing helix angles of the teeth in herringbone gears cancel out the axial thrust, which is generated during gear meshing. This cancellation of axial thrust allows herringbone gears to transmit higher torque without the need for additional thrust bearings or mechanisms. The increased torque capacity of herringbone gears makes them suitable for demanding applications that require high torque transfer.
- Reduced Gear Tooth Deflection: Herringbone gears exhibit reduced tooth deflection compared to spur gears. The double helical arrangement of the teeth in herringbone gears helps counteract the bending forces that can cause tooth deflection. This characteristic allows herringbone gears to maintain a more precise gear mesh, even under high torque loads. The reduced tooth deflection enhances the overall performance and reliability of herringbone gears in high-torque applications.
- Compact Gearbox Design: The high torque capacity of herringbone gears enables the design of more compact gearboxes. The ability to transmit higher torque loads in a smaller package can be advantageous in applications where space is limited. The compact design not only saves space but also reduces the overall weight of the system, making herringbone gears suitable for high-torque applications with size and weight constraints.
- Smooth Operation: Herringbone gears provide smooth and precise gear engagement, even under high-torque conditions. The opposing helix angles of the teeth facilitate gradual meshing and unmeshing, reducing impact and shock loads. The smooth operation minimizes vibrations and noise, which is particularly important in high-torque applications where excessive vibrations can lead to premature wear or component failure.
While herringbone gears offer several advantages for high-torque applications, it’s important to consider other factors such as lubrication, gear material, and system design. Proper lubrication and the use of high-strength materials can further enhance the performance and durability of herringbone gears in high-torque applications. Additionally, system design considerations, such as proper alignment, stiffness, and maintenance practices, should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and longevity of herringbone gears in high-torque scenarios.

Can you explain the unique shape of herringbone gear teeth?
The unique shape of herringbone gear teeth is a defining characteristic of herringbone gears, also known as double helical gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of the unique shape of herringbone gear teeth:
Herringbone gears have a V-shaped or herringbone-shaped tooth profile, which is formed by two helical gear sections that are mirror images of each other. This tooth profile is distinct from the straight or helical tooth profiles found in other types of gears such as spur gears or helical gears.
When viewed from the end, the teeth of a herringbone gear resemble the letter “V”. This shape is created by the combination of two opposing helix angles, one on each side of the gear. The helix angle refers to the angle at which the teeth are inclined relative to the gear’s axis.
In a herringbone gear, the helix angle of one helical section is opposite in direction to the helix angle of the other helical section. This means that as the gear rotates, the teeth on one side lean in one direction, while the teeth on the other side lean in the opposite direction.
The opposing helix angles of the two gear sections in herringbone gears serve several important purposes:
- Axial Thrust Elimination: One of the main advantages of the herringbone gear design is the elimination of axial thrust or end thrust forces. In helical gears, the helix angle of the teeth generates an axial force along the gear’s axis during rotation. However, in herringbone gears, the opposing helix angles cancel out these axial forces, resulting in a balanced gear that does not experience significant axial movement or require thrust bearings.
- Smooth Engagement: The opposing helix angles of herringbone gears facilitate smooth and gradual tooth engagement. As the gear rotates, the teeth on one side gradually come into contact with the teeth on the other side. This gradual meshing reduces sliding friction, minimizes backlash, and ensures a continuous and smooth transfer of power between the gear sections.
- Increased Load Capacity: The V-shaped tooth profile of herringbone gears provides increased tooth contact area compared to gears with straight or helical teeth. This increased contact area improves load distribution and allows herringbone gears to handle higher torque loads, resulting in an increased load-carrying capacity.
The unique shape of herringbone gear teeth requires precise manufacturing techniques to ensure proper meshing and alignment of the gear sections. The teeth must be accurately machined to achieve the correct helix angles and tooth profiles, ensuring smooth operation and efficient power transmission.
In summary, the unique shape of herringbone gear teeth, with their V-shaped or herringbone-shaped profile formed by opposing helix angles, enables axial thrust elimination, smooth engagement, and increased load capacity. These characteristics make herringbone gears well-suited for applications where efficient torque transmission, balanced operation, and high load-carrying capacity are essential.


editor by CX 2024-01-05